
Usually, there is no need to stop the chain reaction promptly. A reactor “ SCRAM” (or “ reactor trip”) is the rapid insertion or fall of the control rods into the core to stop the fission chain reaction. In general, there are two types of reactor shutdown: After criticality is achieved, a positive startup rate is established (the reactor is slightly supercritical), and the power level increases to “ minimum load.” This power increase is then stabilized at minimum load by control rod insertion.Ī reactor is considered shut down when subcritical and sufficient shutdown reactivity exists, so there is no immediate probability of secondary criticality. For the criticality approach, parameters known as estimated critical conditions must be known, and these are target parameters. The process of reactor startup is termed criticality approach or startup to minimum load. A control rod is removed from or inserted into the reactor core to increase or decrease the thermal power.
#Components of nuclear fission reactor generator#
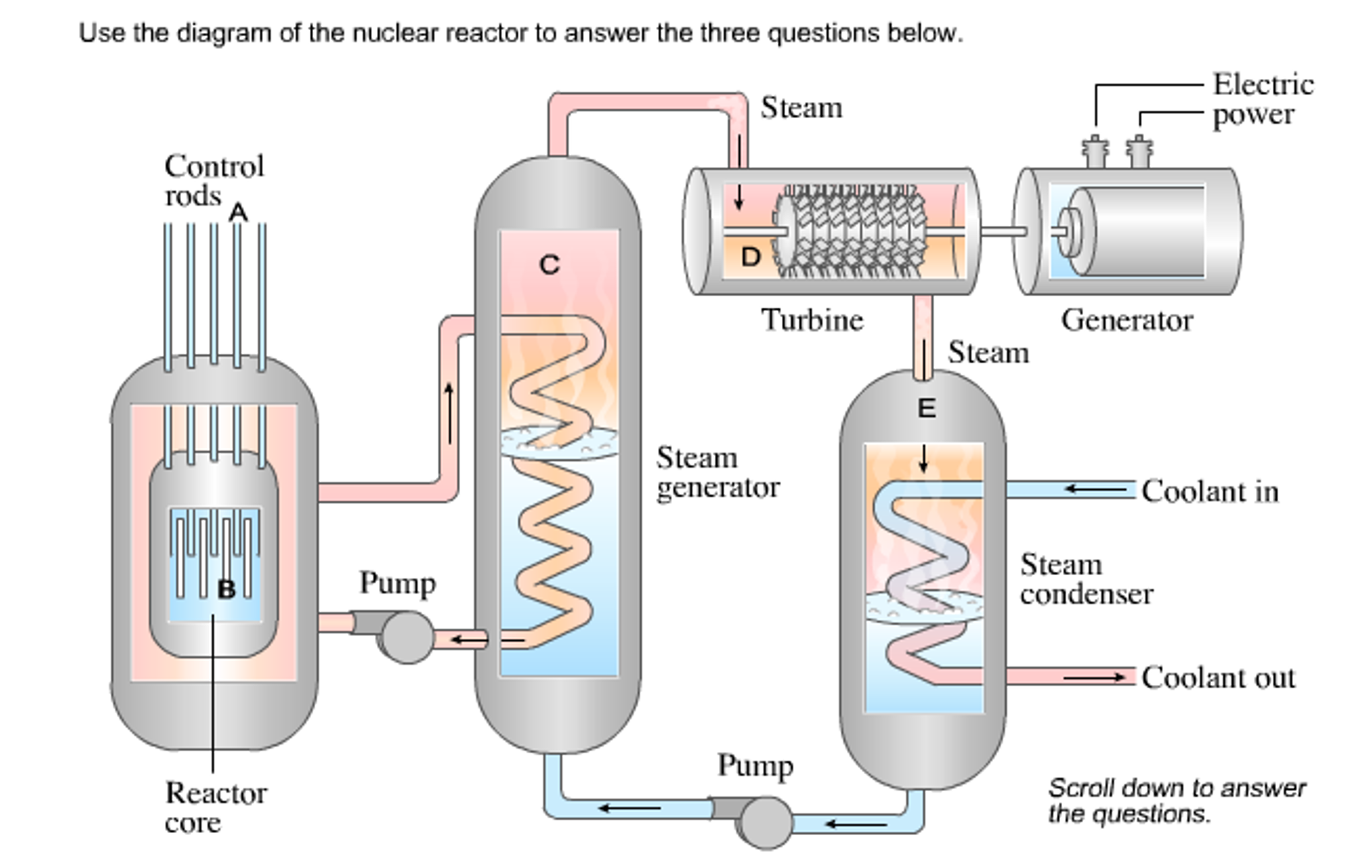
The reactor coolant from the steam generator (primary side) is pumped back into the core through the cold leg, and the process is repeated.This pressurized steam is then routed into the steam turbine, in which steam expands from pressures of about 6 MPa to pressures of about 0.008 MPa.In steam generators, this heat is transferred through the walls of these tubes to the lower pressure secondary coolant located on the secondary side of the exchanger, where the coolant evaporates to pressurized steam ( saturated steam 280☌ 536☏ 6,5 MPa).Hot coolant goes to hot legs and is pumped via main coolant pumps into steam generators.For PWRs, the coolant (water) is heated in the reactor core from about 290☌ (554☏) to approximately 325☌ (617☏) as the water flows through the core.
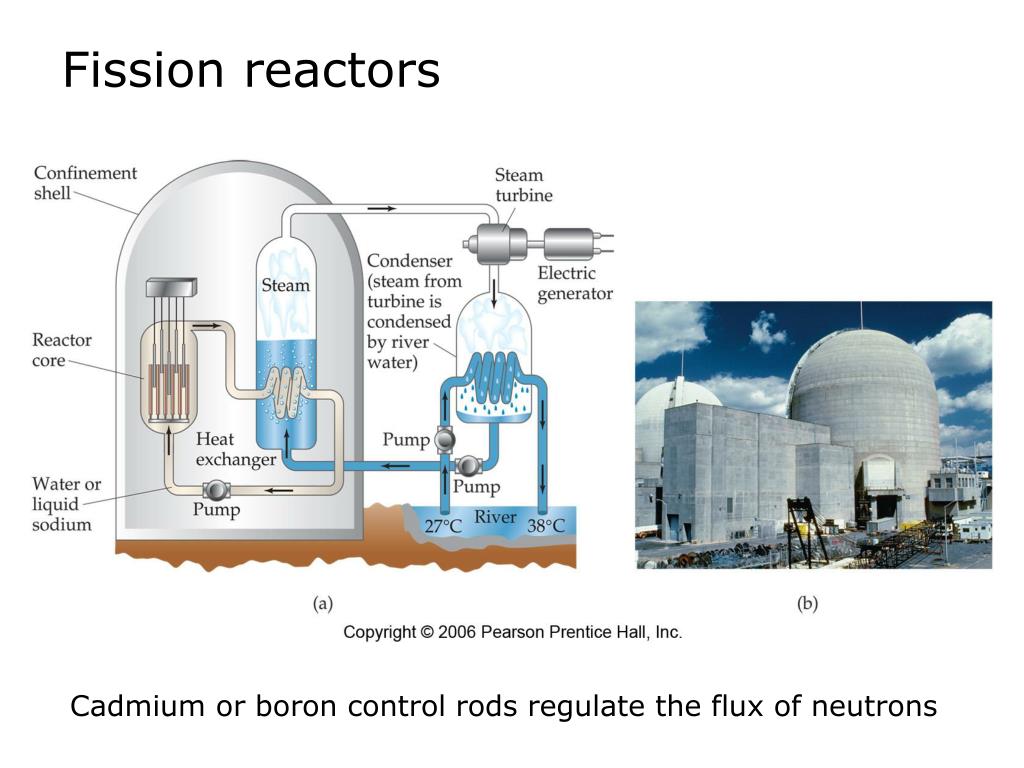
Typical reactor nominal thermal power is about 3400MW, but the heat produced must be continuously removed from the core.The reaction rate of this chain reaction corresponds to the nominal thermal power.In nuclear reactors, usually, control rods are used for maintaining the desired state, which means a self-sustaining chain reaction.This condition is known as the critical state. In that case, there is no change in neutron population in time (i.e., the reactor is stable), and the chain reaction will be self-sustaining. Suppose the multiplication factor for a multiplying system is equal to 1.0. The basic classification of states of a reactor is according to the multiplication factor. In nuclear reactors, control rods are used for maintaining the desired state of fission reactions.Therefore the typical thermal efficiency of its Rankine cycle is about 33%. Typical reactor nominal thermal power is about 3400MW, thus corresponding to the net electric output of 1100 MW.A typical reactor may contain about 100 tonnes of enriched uranium (i.e., about 113 tonnes of uranium dioxide).


Nuclear reactors in nuclear power plants are “only” used to generate large amounts of heat.The main product of research reactors is usually a neutron flux, which is then used, for example, for medical purposes or research purposes.The reactor core contains the nuclear fuel (fuel assemblies), the moderator, and the control rods. The reactor core is a bounded region where neutron multiplication and chain reactions occur. The key component of nuclear reactors is a reactor core.
Since nuclear reactors are used in nuclear power plants, research facilities, or nuclear-propelled ships, their output is thermal energy, or they can be used as a source of neutron radiation. Generally, a nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a self-sustained nuclear chain reaction. Article Summary & FAQs What is a nuclear reactor?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
